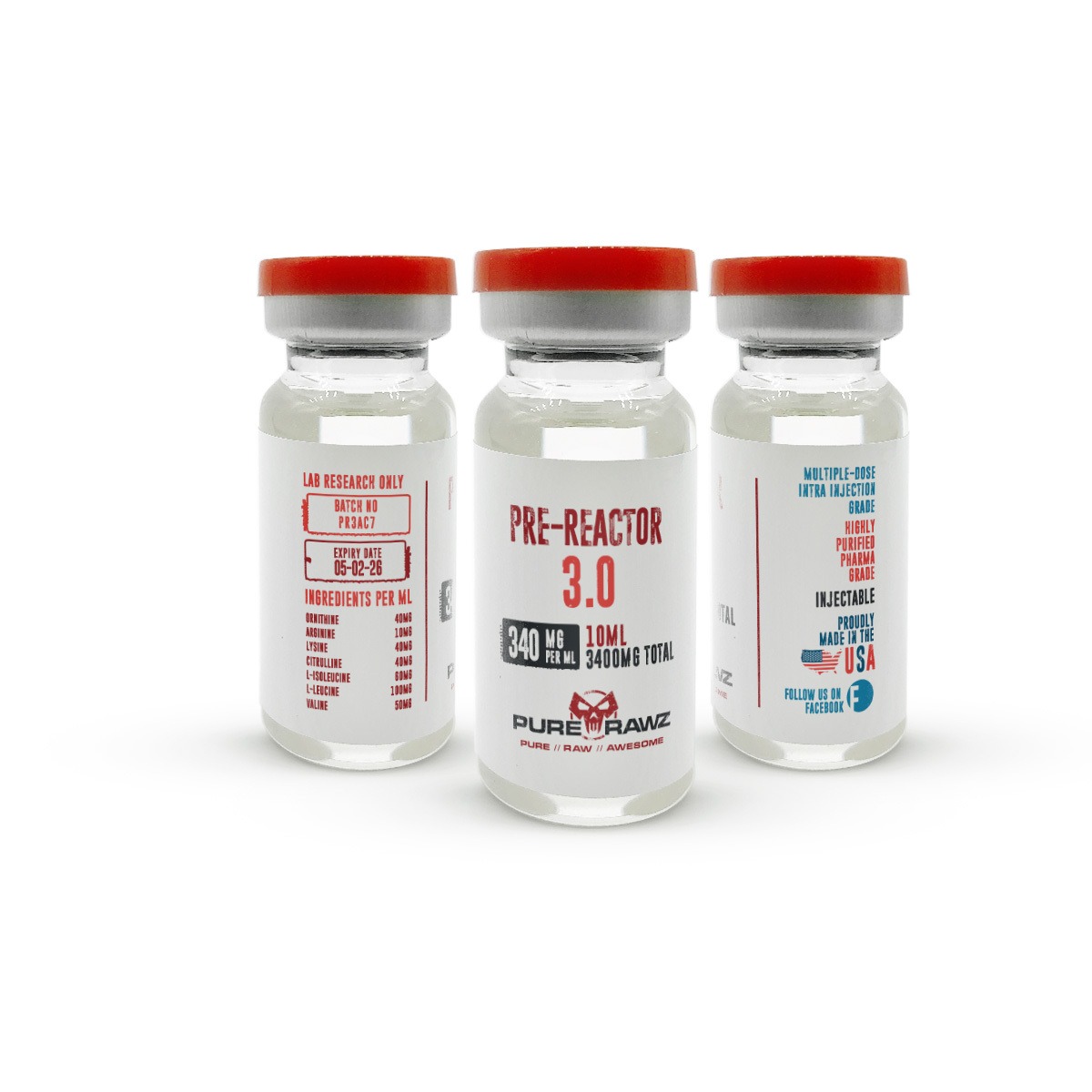
Pre-Reactor 3.0 injectable (Ornithine + Arginine + Lysine + Citrulline + L-Isoleucine + L-Leucine + Valine)
$203.24
Earn 203 points upon purchasing this product.
- 1st and 3rd Party Verified for 99% Purity
- Free Shipping on Orders Over $100+
Enjoy 24/7 customer support, 1st & 3rd party verified 99% purity, and free shipping on orders over $100!
Description
Pre-Reactor 3.0 injectable (Ornithine + Arginine + Lysine + Citrulline + L-Isoleucine + L-Leucine + Valine) – Product Information
Pre-Reactor 3.0 is an injectable research product meticulously formulated for scientific investigations into exercise-related physiological responses. This research compound, containing key amino acids, aims to contribute to the understanding of potential physiological effects. Purerawz sells Pre-Reactor 3.0 strictly for research purposes, and this injectable is not intended for human consumption.
- Pre-Reactor 3.0 injectable consists of Ornithine (40mg), Arginine (10mg), Lysine (40mg), Citrulline (40mg), L-Isoleucine (60mg), L-Leucine (100mg), and Valine (50mg).
- Pre-Reactor 3.0 is offered in 340mg per ml for 10ml, totaling 3400mg.
What is Pre-Reactor 3.0 injectable (Ornithine + Arginine + Lysine + Citrulline + L-Isoleucine + L-Leucine + Valine)?
Pre-Reactor 3.0 introduces a unique Injectables research product specifically created for investigations in exercise physiology. Available in a 10ml presentation, this compound blends Ornithine (40mg), Arginine (10mg), Lysine (40mg), Citrulline (40mg), L-Isoleucine (60mg), L-Leucine (100mg), and Valine (50mg), offering researchers a unique platform for in-depth exploration into the intricate interplay of these amino acids during the pre-workout phase. Prioritizing aspects such as vasodilation, nitrogen balance, and metabolic processes, the compound opens new avenues for comprehensive research into both individual and synergistic effects. Exclusively designed for research purposes, Pre-Reactor 3.0 strives to contribute valuable insights to the scientific understanding of exercise-related physiological responses.
How Does Pre-Reactor 3.0 Work?
Ornithine
Ornithine emerges as a pivotal non-protein amino acid, assuming a critical role within the urea cycle, a metabolic pathway intricately involved in detoxifying ammonia, a byproduct stemming from protein metabolism. Within the dynamic urea cycle, ornithine orchestrates a vital union with ammonia, giving rise to citrulline and subsequently transforming into arginine. This intricate conversion process serves as a key mechanism for eliminating excess nitrogen in the form of urea, ultimately excreted through urine.
In the realm of research, ornithine takes center stage for its exploration of potential effects on reducing ammonia levels, a factor that tends to accumulate during intense physical exertion, contributing to the onset of exercise-induced fatigue. The remarkable capability of ornithine to facilitate the efficient removal of ammonia introduces implications for fatigue mitigation and support for overall exercise performance. Thus, ornithine stands as a subject of profound interest in the extensive exploration of exercise physiology and metabolic pathways. The multifaceted role it plays in the urea cycle underscores its significance, providing researchers with an intriguing avenue for understanding and optimizing physiological responses in the context of strenuous physical activity. [R]
Arginine
Arginine, a semi-essential amino acid, assumes a versatile role in various physiological functions, capturing attention in the realm of research for its pivotal role as a precursor to nitric oxide (NO), a signaling molecule endowed with potent vasodilatory properties. Within the body, Arginine undergoes conversion into NO facilitated by enzymes known as nitric oxide synthases (NOS). This transformation sets in motion a cascade wherein nitric oxide acts to relax and dilate blood vessels, thereby enhancing blood flow and optimizing nutrient delivery to tissues.
The research spotlight on Arginine is particularly directed at unraveling its vasodilatory effects, delving into their potential implications for cardiovascular health and exercise performance. The augmented blood flow orchestrated by nitric oxide opens avenues for investigation into its impact on muscle oxygenation, nutrient transport, and the efficient removal of metabolic byproducts during physical activity. Furthermore, Arginine’s engagement in protein and collagen synthesis elevates its significance in studies focused on tissue repair and overall metabolic function. Researchers are engaged in a nuanced exploration of the intricate mechanisms through which Arginine contributes to these physiological processes, seeking a comprehensive understanding of its role in health and its potential applications across diverse contexts. [R]
Lysine
Lysine, classified as an essential amino acid, holds significance in the research domain owing to its indispensable role in diverse physiological processes. Its essential nature stems from the fact that the human body cannot synthesize it independently. Of particular research interest is Lysine’s pivotal involvement in protein synthesis, serving as a foundational building block for the intricate construction of proteins. Beyond its contribution to general protein formation, Lysine assumes a critical role in the creation of collagen, which is an essential structural protein vital for the integrity of connective tissues, skin, and bones. The exploration of Lysine’s intricate functions contributes not only to a nuanced understanding of fundamental biological processes but also holds potential implications for areas such as tissue repair and overall structural integrity in various biological contexts. [R]
Lysine is also known for its interactions with other amino acids and its role in supporting the immune system. It competes with arginine for absorption and cellular uptake, and this interaction is explored in research related to viral infections as some viruses rely on arginine for replication. [R]
Within the domain of exercise physiology research, Lysine becomes a subject of exploration, with a focus on unraveling its potential to bolster protein synthesis, facilitate tissue repair, and fortify immune function amid periods of physical exertion. The intricate interplay of Lysine, in conjunction with other amino acids, becomes a focal point for researchers as they strive to comprehend its comprehensive impact on the physiological response to exercise. The inquiry extends to whether Lysine plays a discernible role in optimizing both performance and recovery in the dynamic realm of physical activity. By delving into these mechanisms, researchers aim to uncover valuable insights that could potentially enhance our understanding of how Lysine contributes to the intricate balance of factors influencing exercise-induced adaptations and overall well-being.
Citrulline
Citrulline, a non-essential amino acid, assumes a pivotal role in the urea cycle, contributing significantly to the elimination of ammonia, a byproduct resulting from protein metabolism. In a transformative process, Citrulline undergoes conversion into another amino acid, arginine, within the kidneys. Arginine, in its own right, serves as a precursor to nitric oxide (NO), a molecule intricately involved in diverse physiological processes, notably vasodilation and the relaxation of blood vessels.
In the realm of research, Citrulline has become a subject of intensive study, particularly for its potential benefits in cardiovascular health and exercise performance. The augmentation of arginine levels through Citrulline supplementation emerges as a key focus, as it holds the potential to amplify nitric oxide production, culminating in enhanced blood flow. This vasodilatory effect is theorized to optimize the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to actively engaged muscles during exercise, potentially mitigating fatigue and fortifying overall endurance. The investigation into Citrulline’s dynamic interplay with arginine unveils a promising avenue for enhancing our understanding of its physiological implications, presenting opportunities for refining approaches to cardiovascular support and maximizing exercise-related performance outcomes. [R]
Citrulline’s role in the urea cycle and its connection to nitric oxide production make it a subject of interest in research exploring its impact on exercise-induced fatigue, muscle recovery, and overall cardiovascular health.
L-Soleucine
L-Soleucine, classified as an essential amino acid, assumes a pivotal role in the intricate process of muscle protein synthesis, actively contributing to the growth and repair of muscle tissue. As a distinguished member of the branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) family, L-Soleucine collaborates synergistically with its counterparts, such as L-Leucine and Valine, to form a dynamic trio that is instrumental in the comprehensive study of overall muscle function and performance. Within the formulation of Pre-Reactor 3.0, L-Soleucine imparts its distinctive attributes to create a harmonious blend, fostering an exploration into the potential benefits of muscle optimization.
It is crucial to underscore that the information provided here is exclusively intended for research purposes and is not intended for actual use.
L-Leucine
L-Leucine, a distinguished member of the branched-chain essential amino acids, commands a prominent role within the expansive domain of amino acids, particularly in the context of muscle protein synthesis. As an essential amino acid, L-Leucine is characterized by its inability to be synthesized within the body, necessitating its acquisition through dietary sources. Amid the family of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), L-Leucine takes center stage, demonstrating notable potential in fostering muscle growth and repair. Serving as a crucial regulator in the intricate process of protein synthesis within muscle tissues, L-Leucine assumes a pivotal role in the overarching objective of developing and sustaining muscle mass. Collaborating seamlessly with other essential amino acids, L-Leucine orchestrates complex mechanisms that drive the synthesis of proteins vital for the optimal function of muscles. It is imperative to emphasize that this information is exclusively intended for research purposes and is not meant for actual use, underscoring the investigational nature of the compound and its contribution to advancing scientific understanding in the realm of muscle physiology.
Valine
Valine, designated as an essential amino acid, holds noteworthy potential in diverse physiological processes, particularly in the realm of muscle metabolism and potential repair. As an integral member of the branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), alongside leucine and isoleucine, valine emerges as a key player in the intricate dynamics of protein synthesis and the potential preservation of muscle tissue. Notably, essential amino acids like valine cannot be endogenously produced by the body, underscoring the potential need for their acquisition through dietary sources or supplementation.
Characterized by its unique structural attributes, valine is poised to contribute significantly to maintaining the delicate balance of amino acids requisite for protein synthesis and the potential promotion of muscle growth. Beyond these roles, valine is believed to be actively involved in energy production, offering potential regulatory benefits to the immune system and serving as a potential source of fuel for muscles during periods of intense physical activity. It is crucial to clarify that the provided information is exclusively intended for research purposes and does not imply actual usage or established claims. This distinction reinforces the investigational nature of valine and its role in advancing scientific knowledge within the context of physiological processes and muscle function.
In a research context, the comprehensive study of compounds such as Ornithine, Arginine, Lysine, Citrulline, L-Isoleucine, L-Leucine, and Valine together could involve investigating their collective impact on muscle protein synthesis, tissue repair, exercise performance, vasodilation, cardiovascular health, metabolic pathways, energy production, immune system modulation, and overall physiological responses. Employing a multi-disciplinary approach, researchers may explore their potential synergistic effects and interactions, utilizing in vitro studies, animal models, and controlled human trials. Metabolomic analyses and systems biology approaches can provide insights into the intricate network effects within biological systems. Ultimately, such a comprehensive investigation aims to enhance our understanding of the combined physiological roles of these compounds, offering valuable insights for potential applications in exercise physiology, metabolic health, and overall well-being. Ethical considerations and adherence to research guidelines remain paramount throughout these studies.
Potential Research Applications
Pre-Reactor 3.0 is designed exclusively for research purposes, aiming to contribute to the understanding of amino acid interactions and their potential effects on physiological responses during exercise physiology.
Vasodilation
The blend of ornithine, arginine, lysine, and citrulline in Pre-Reactor 3.0 is theorized to contribute to vasodilation through various mechanisms. Arginine and citrulline take center stage as crucial contributors to nitric oxide (NO) synthesis, a potent vasodilator. The conversion of arginine to NO induces the relaxation of blood vessels, resulting in heightened blood flow. Although ornithine doesn’t directly participate in NO synthesis, its indirect involvement in supporting vasodilation is suggested. Serving as a precursor to arginine, ornithine’s availability may influence the overall arginine-NO pathway. Additionally, lysine, another constituent in the formulation, is implicated in this process, with studies proposing that lysine supplementation may augment the effects of arginine on NO production.
Nitrogen Balance
The amalgamation of ornithine, arginine, lysine, and citrulline within Pre-Reactor 3.0 is postulated to bear significance for nitrogen balance within a research framework. Nitrogen balance, serving as a gauge for the body’s nitrogen intake compared to nitrogen excretion, plays a pivotal role in assessing physiological states. A positive nitrogen balance, indicative of the body retaining more nitrogen than it excretes, is often linked with an anabolic state. This state has potential implications for supporting processes such as muscle protein synthesis, reflecting a scenario favorable for the growth and maintenance of muscle tissue. In the context of research, exploring the impact of this combination on nitrogen balance offers insights into its potential role in fostering an environment conducive to anabolic processes. [R]
Arginine, ornithine, and lysine are essential amino acids involved in various aspects of protein metabolism. Arginine and ornithine contribute to the urea cycle, which plays a role in nitrogen excretion. Lysine is essential for protein synthesis, and its availability can influence the overall balance of nitrogen.
Energy Production
Arginine and citrulline are involved in the production of nitric oxide (NO), a signaling molecule that can enhance blood flow and nutrient delivery. This improved circulation may contribute to more efficient energy production. [R]
Muscle Metabolism Studies
In the realm of muscle metabolism, researchers may embark on an exploration of the specific combination of L-Soleucine, L-Leucine, and Valine, aiming to unravel their collective impact on crucial facets such as protein synthesis, energy production, and overall muscle health. Leucine, positioned as a pivotal regulator in the intricate orchestration of muscle metabolism, assumes a central role in governing protein synthesis through the mTOR pathway. Beyond its influence on protein synthesis, leucine showcases an additional dimension by inhibiting autophagic proteolysis via an mTOR-independent pathway.
Recent insights into the metabolic dynamics of isoleucine, a positional isomer of leucine, reveal its remarkable efficacy in preventing a surge in plasma glucose levels. Strikingly, isoleucine outperforms leucine and valine in oral glucose tolerance tests conducted on normal rats. The spotlight on isoleucine intensifies, particularly due to its insulin-independent stimulation of glucose uptake in C2C12 myotubes. This comprehensive examination of the combined effects of these amino acids offers a nuanced understanding of their roles in shaping muscle metabolism and potential implications for glucose homeostasis. [R]
Lean Muscle Mass Preservation during Caloric Restriction
During periods of calorie restriction, BCAAs may have the potential to help preserve lean muscle mass by providing an alternative energy source, sparing muscle protein breakdown. According to research, Leucine, in particular, plays a crucial role in this preservation. [R]
Summary
Pre-Reactor 1.0 stands as a valuable tool in the realm of exercise physiology research, offering a synergistic blend of amino acids for in-depth scientific investigations. Researchers employing this Injectable compound are encouraged to adhere strictly to ethical research practices and safety protocols as they explore the potential impacts of these ingredients on exercise-related physiological responses.
Frequently Asked Questions
How should Pre-Reactor 3.0 be stored for research purposes?
Store Pre-Reactor 3.0 in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight. Proper storage conditions are crucial to maintaining the stability of the compounds during the research period. Ensure that the product is securely sealed and protected from environmental factors that may compromise its integrity.
Is there existing research on the individual components of Pre-Reactor 3.0?
Yes, individual components such as ornithine, arginine, lysine, and citrulline have been subjects of scientific research. Researchers are encouraged to review relevant literature to understand the individual characteristics and effects of each component before conducting studies with Pre-Reactor 3.0. Research on potential interactions with other substances is ongoing. It is advisable to conduct comprehensive studies to understand any possible interactions with different compounds.
What is the potential impact of Pre-Reactor 3.0 on blood pressure in research studies?
Exploring the impact of Pre-Reactor 3.0 on blood pressure presents a captivating avenue of research, particularly given the inclusion of arginine and citrulline, which are acknowledged for their potential involvement in vascular function. Previous studies delving into these components have revealed connections with the modulation of blood pressure, prompting researchers to delve into the nuanced mechanisms contributing to these effects. This investigation holds promise in unraveling the intricate interplay between the formulation’s ingredients and blood pressure regulation, providing valuable insights into their potential cardiovascular implications.
Can histone lysine methylation be a focus of research when studying Pre-Reactor 3.0?
Although not the primary focus, researchers might contemplate a more expansive exploration of the comprehensive impacts of amino acids, including lysine, on cellular processes, potentially extending to epigenetic modifications such as histone lysine methylation. A systematic investigation into these molecular pathways holds the potential to yield valuable insights into the broader cellular effects orchestrated by Pre-Reactor 1.0. This approach seeks to uncover intricate connections between the formulation’s amino acid components and molecular events, shedding light on their potential roles in influencing epigenetic processes and contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of cellular responses.
Can Pre Reactor 3.0 be used in animal studies?
Pre Reactor 3.0 may be suitable for animal studies, but researchers should adhere to ethical guidelines and regulations when conducting experiments involving animals.
Where Can I Buy Pre-Reactor 3.0 Online?
PureRawz sells the highest purity of Pre-Reactor 3.0 online!
To ensure good quality as a research chemical efficient supplier, we include reference materials with each product and provide strict quality control standards to be free from potentially harmful levels of contaminant with an independent Certificate of Analysis from a third party for identification, purity, and concentration verification.
We offer free international shipping on all orders above $100. You can pay for your purchase through various methods like crypto and credit card. Our product range consists of liquid, powder, and capsule formulations of TUDA, all of which are equally exceptional in quality.
Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. THE PRODUCTS DESCRIBED HEREIN ARE FOR LABORATORY AND RESEARCH USE ONLY.
All clinical research must be conducted with oversight from the appropriate Institutional Review Board (IRB). All preclinical research must be conducted with oversight from the appropriate Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC), following the guidelines of the Animal Welfare Act (AWA).
Our content is intended to be used and must be used for informational purposes only. It is very important to do your analysis and research from Trusted Sources before making any purchase based on your circumstances. You should independently research and verify any information that you find on our Website and wish to rely upon.
By completing and paying for your order, you agree to our Terms and Conditions. Customer satisfaction is our number one priority. If you are not 100% satisfied with the product you received, please contact us at support@purerawz.co
ATTENTION: All our products are for LABORATORY AND RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY, not for veterinary or human usage.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet